Introduction
Fawn is the second in the Tier 0 Starting Point machines. This is another educational system, so I will cover the commands in-depth than I will in future machines, but will build off knowledge from the previous machine, Meow.
tl;dr
Spoiler!
1. `FTP` to target.2. username "anonymous".
3. `GET` flag to localhost.
4. ????
5.

Establishing a Connection
Spawn the bastard and get vpn going.
I’ve confirmed the target is reachable with a ping.
Initial Scan
Unlike the last machine, let’s do our default nmap scan now and store the results in recon/all again and move on to the tasklist.
The Tasklist
Task 1
What does the 3-letter acronym FTP stand for?
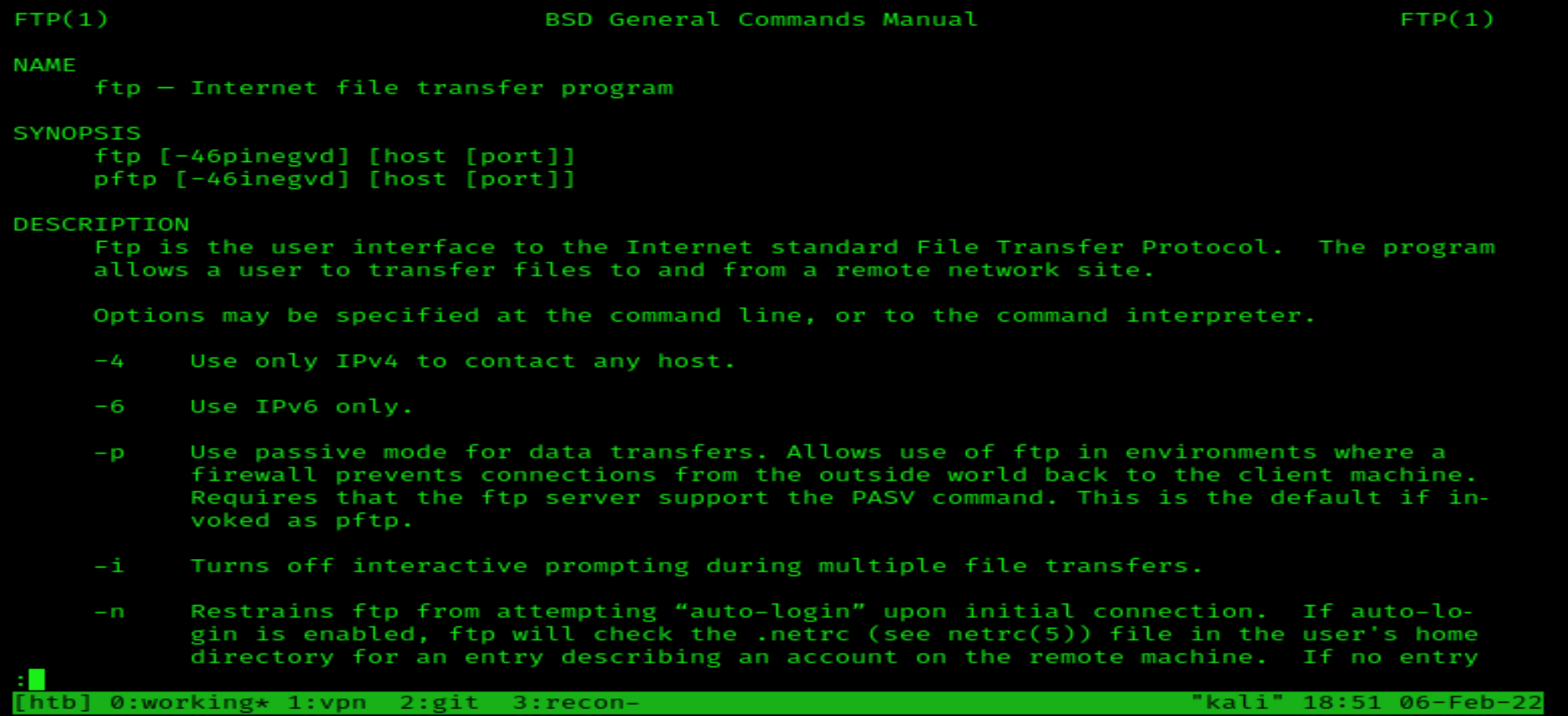
The next couple of questions are related to FTP. Let’s run man ftp | less.
We can see the description for FTP is ‘an internet file transfer program’. However, the answer we are looking for is further on and is File Transfer Protocol.
Task 2
What communication model does FTP use, architecturally speaking?
FTP uses the client-server model. In this model, clients typically are endpoint systems used by people to conduct tasks and look at Reddit. Servers can also be endpoint systems, but are typically standalone systems that run the FTP service for client(s) to connect and upload/download files.
Task 3
What is the name of one popular GUI FTP program?
FileZilla is a widely used GUI FTP program.
Task 4
Which port is the FTP service active on usually?
FTP runs off port 23/TCP by default.
Task 5
What acronym is used for the secure version of FTP?
Secure FTP is known as SFTP. Crazy right?
Our First Scan
Task 6
What is the command we can use to test our connection to the target?
We should already know that this tool is the ping command.
Task 7
From your scans, what version is FTP running on the target?
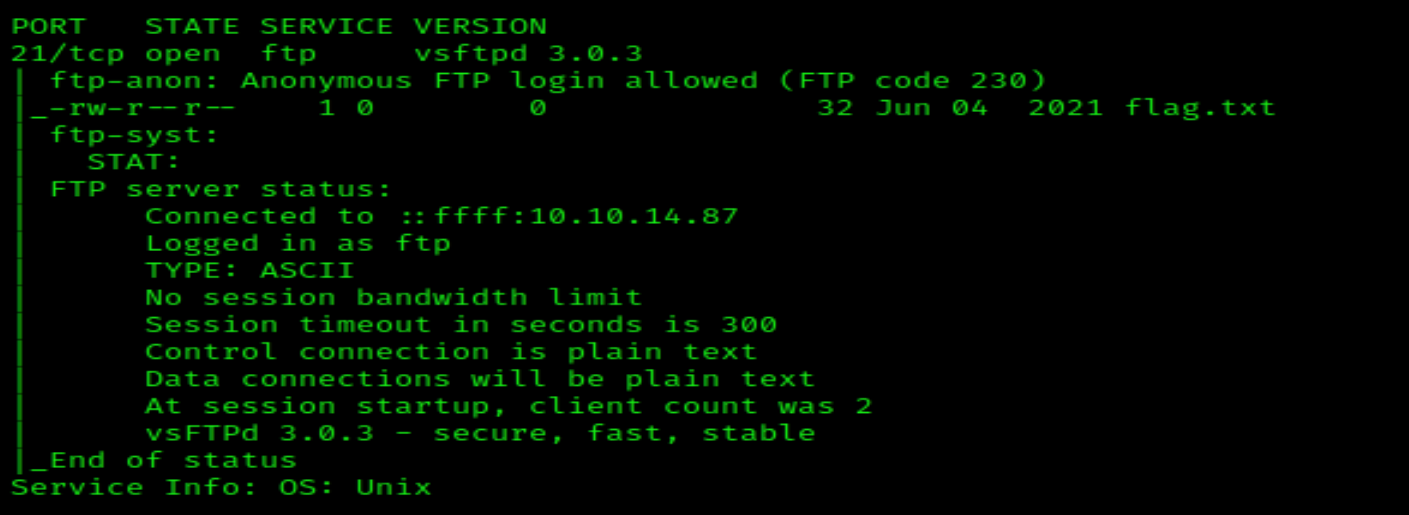
Let’s take a look at our scan results from earlier (remember you can use cat [filename] | less to print the contents of a file in a paginated fashion if you stored your results in a file).
We ran nmap with the -A flag earlier, which runs service detection (among other things).
We always want to pay attention to the section below that details detected services and ports:
It looks like the service vsftpd is running version 3.0.3.
Task 8
From your scans, what OS type is running on the target?
At the bottom of our scan results, we have data labeled Service Info. The OS is detailed as Unix.
Task 9
Submit root flag
Now we have to get the flag, let’s review some important info:
What do we know?
flag.txtis located on teh FTP server.- The
FTPservice allowsanonymous logins.
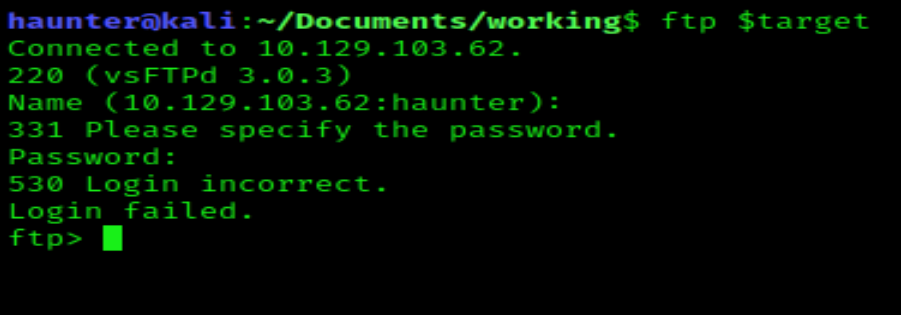
Anon login is good to see. Let’s try to connect.
I tried authenticating without entering a username or password. This is clearly not what anonymous login means. Shit.
Whever you need info, always check the tools man pages first.
We are searching for the string "user" in a hope that there will be a command filter or flag related to logging in with a user account, and any special syntax needed for the command.
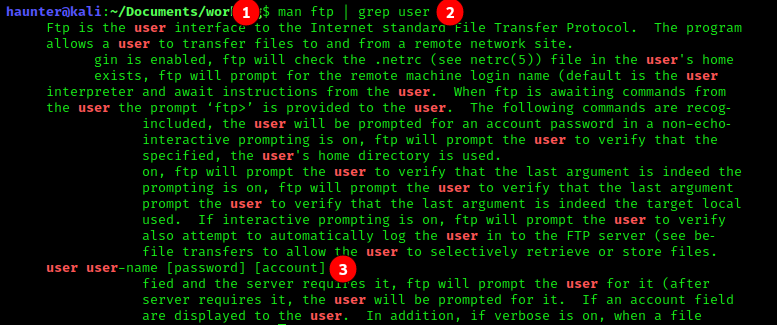
We run man for ftp (1), but for the sake of expediency we then pipe the output and use grep to search through the output for the term "user" (2). grep is an extremely useful tool used for searching for patterns, and this is a very basic use case involving a simple string. At the bottom of our filtered output (3), we can see that there is an FTP-specific command user. This command is entered on the ftp interface and will then prompt for a username to login with.
With that knowledge, let’s give it a try:
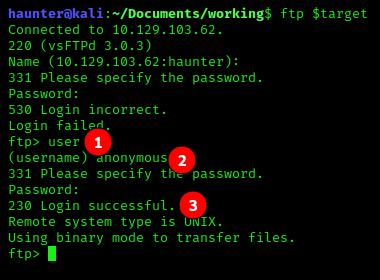
- We enter the
usercommand at theftpinput prompt. - The prompt then asks for a username, we enter
anonymousand do not enter a password. - We have joy- we are now on the FTP server.
Capturing the Flag
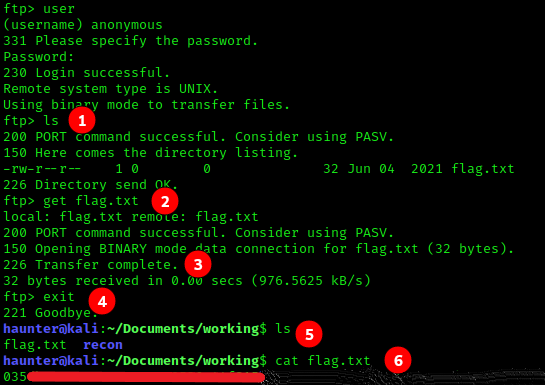
- First thing to do is look at our current directory with
ls. There is one file listed- ourflag.txt. - If you try to
catthe contents of theflag.txtfile, you may get an error. Remember that some tools that are available on your local system may not be installed on a remote system. We useget flag.txtto download the file to oour local system in this case. - The file downloads successfully, let’s get the contents.
- Use the
exitcommand to terminate the FTP session - With a local
ls, we see thatflag.txtwas downloading in the directory we initiated the FTP session in. - We
catthe flag and have ownedFawnsuccessfully.

Lessons Learned
Anonymous FTP allowedon annmapscan is a good potential foothold vector